If ever there is a time when a system absolutely cannot fail, it’s your emergency shut down safety system during an event. These systems are critical to minimizing the impact of potentially disastrous situations such as fire, process irregularities, or storms.
The solenoid valve, frequently taken for granted as a commodity, is actually an essential component in the Emergency Shut Down system. How the solenoids function can mean the difference between a successful emergency shut down or failure. Failure can result in loss of life, an environmental catastrophe, and/or significant financial loss for your organization.
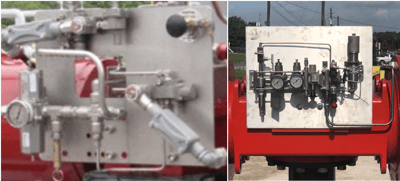
Solenoid reliability is crucial as emergency shut down situations count on dependable performance. Based on Versa’s 70 years of experience creating the industry’s most reliable valves, we’ve pulled together a few key considerations when selecting a solenoid valve for your mission-critical application.
1. Solenoid Type: Direct Acting Solenoid or Direct Acting Solenoid - Pilot Valve
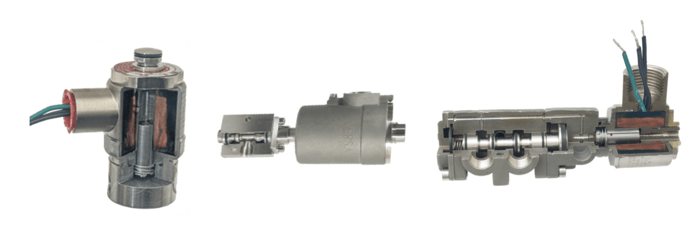
Much discussion centers on which type of valve is more reliable and, fortunately, Versa offers full lines of both types. The answer depends on the application’s flow requirements. If installation and maintenance is in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations for low-flow applications (less than .5Cv), some say the best choice is a direct acting solenoid due to the limited number of parts. For higher flow applications, there is no better choice than the Direct Acting Solenoid integrated onto a pilot valve. This option enables using a low watt (as low as 0.5 watt) solenoid to obtain a flow rate from 0.5 to over 13Cv. The return spring force of these valves is unparalleled which ensures a positive return shift.
Note: Due to the low-flow characteristics of the direct acting solenoid, it is often tubed to a higher flow pilot valves for ESD applications.
2. Ingress of the Solenoid Valve

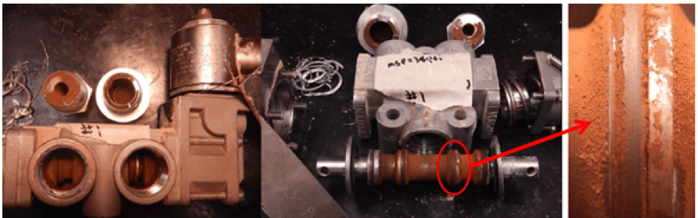
Reducing opportunities for contaminates to enter the valve is paramount for the reliable functions of the solenoid valve. Most manufacturers recommend clean media with a 40-micron filter element. It’s also recommended that the filter be placed directly before the valve for ESD applications to trap contaminates lodged in the airlines from entering the solenoid.
Other areas of ingress are through the exhaust ports. There may be multiple exhaust ports depending on the type and function of the solenoids. Selecting a dust excluder will stop the ingress of particulate or insects while maintaining exhaust flow. Unfortunately, bug screens allow dirt to enter and adhere to internals and sintered filters clog frequently. Versa offers an alternative flapper type design, which acts like a check valve to prevent this from happening.
3. Exercising the Solenoid
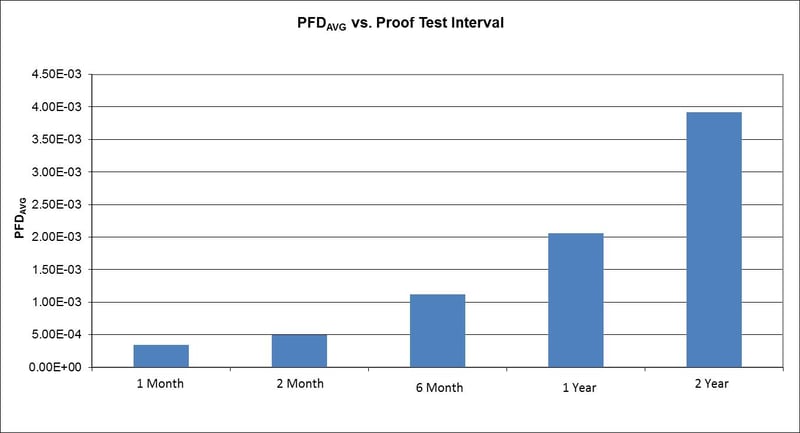
Solenoids cycle infrequently on ESD applications. The more the solenoid valve is cycled, the more reliable the ESD will perform. Versa options such as solenoid bypass circuits, redundant solenoids, and partial valve stroke facilitate exercising the solenoid while maintaining the process flow.
4. Reliability Options

Versa offers a myriad of additional options to tailor the solenoid valve to the requirements of your specific application, such as SIL compliance, flow, temperature, media type and environmental conditions. Contact Versa for details on our unique offerings to ensure reliability in your mission-critical application.



